HVAC: Efficient air conditioning. The energy of the future

The term airthermy is certainly fashionable in the world of air conditioning. If you've recently changed your heating or air conditioning system, you've probably heard about it. If you are looking for a home, you have probably been informed. Even if you are completely aware of this scene, you may have heard about this technology at some point. But do you really know what it is?
With an airthermy, heat, cold and sanitary hot water (ACS) can be produced by means of a single equipment in a clean and cheap way. The air conditioning of the future is already here.
1. Renewable energy Technology
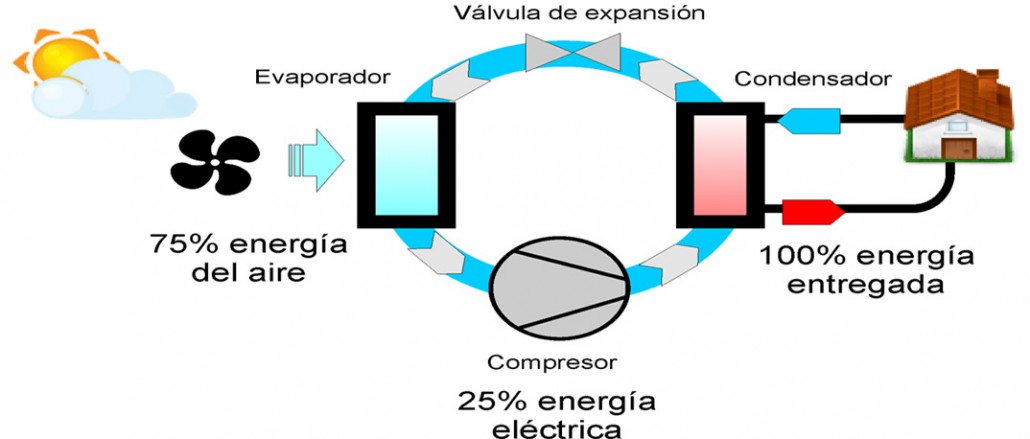
The energy provided by the air-thermics comes from 75, 5% of the external airborne and only 25% comes from electricity consumption. So it is a technology that can be considered renewable energy, as we will see below.
In the world of air conditioning, the air-thermal is basically a technology that mainly uses the energy of the airspace to air the spaces. In general, it is considered as a clean and highly efficient source of energy.
The performance of the heat pumps, marked by the COP, is usually always higher than 2.5 (arriving generally up to 4 or 5), meaning that for each electric kw consumed could obtain up to 3 kw thermal, a fact that gives us the idea that they are teams very Efficient.
2. Low CO2 emissions
Very low CO2 emissions can be imputed for each thermal kWh generated. They can go down to 50% or emissions from traditional energies.
According to a study by GreenPeace in Spain, a medium heat pump generates emissions of 71grCO2/kwh, while the average of a natural gas boiler is 215grCO2/kwh.
Achieves a significant reduction in CO2 emissions from conventional energies. It also uses the ecological refrigerants R410A, R134a and R744 which have a null impact on the ozone layer.

3. Cold, heat and ACS in a single equipment
One of its main advantages and the key to the wind is that it works with a single generator for three types of applications: heating, sanitary hot water (ACS) and refrigeration. This clearly leads to simplicity in the installation and a reduction in the number of equipment and air conditioning systems to be installed in the house, as well as having ACS.
For the heating function, the diffusion of the energy can be carried out by means of low temperature radiators, heat diffusers (splits, fancoils, etc.) or by radiant floor. The cooling function can be done by means of heat diffusers, or walls or refreshing roof.
The sanitary hot water can be stored in a tank and is obtained by heating in double stage or with support of solar thermal plates.

4. Cheap, comparative energy with other energies
Since the air-thermal energy is used as a power source, a free renewable energy and available 24 hours a day, its advantages compared to other traditional systems are very significant. You can see the effective average price for different fuels this last winter:
Propane: 0.119 euros/kWh
Diesel oil: 0.080 euros/kWh
Natural Gas: 0.068 euros/kWh
(COP average 4): 0.053 euros/kWh
In addition, equipment with air-to-water heat pumps lacks a burner and combustion chamber, so there is no residue during operation that requires cleaning operations.
We can purchase a monobloc or bibloc airthermy equipment. Monobloc systems are more economical when buying but require a hot water tank. However, the installation price of the BIBLOC system is a bit larger (because both blocks must be connected) but it is not a big difference in quantity and has the advantage that with a single equipment we can obtain general air conditioning of a house (water ACS , cold and heat). We can complement our air-thermal system with radiant floor or low temperature fancoils.
The prices of the equipment of airtherms are around the 5,000-10.000 euros (cost of the installation not included) so that the amortizations can be fast.
5. Compact, modular and easy-to-install equipment
Although it is ideal for new construction dwellings, it is easily adapted to dwellings in buildings already built with a previous air conditioning system. These units occupy the same space as a wall or on-floor boiler, but with the great advantage that they do not require fuel storage space or gas exhaust ducts, reducing the necessary physical space and increasing Housing security.

6. Differences with traditional air conditioning
The term "energy stored in the form of heat in the ambient air" is defined. To do this, a transfer system is used composed of two elements: an outdoor unit that captures the calories, and an indoor unit that is transferred to a water circuit of "central heating" type. The transport of these calories is charged with a refrigerant fluid circulating between both units and which is driven by a compressor. " The thermal technology is used as a housing thermal conditioning, because you can capture this free energy and use it to heat a house or any other building.
The traditional ' air-conditioning ' is an air-to-air heat pump system, which extracts the heat from the outside air and transmits it to the interior of the house. Almost all systems of this type already use the inverter technology (which allows to adapt the temperature) but present the disadvantages, in front of the air-thermics, of a) higher economic cost by electricity, b) noise generation and air currents C) does not include ACS. Therefore, the air-water heat pumps (thermal systems) that obtain the heat from the outside air and transmit it to a hot water circuit are becoming more popular, producing 4 times more energy than it collects for the most part free.

7. Do you have any drawbacks?
In addition to the advantages explained above, it is necessary to take into account the possible drawbacks of this technology in some circumstances:
- Loss of performance in very cold weather zones: in areas with freezing temperatures for long periods, it may be necessary to have double stage equipment, complementation with solar panels or to think of alternatives such as Geothermics.
- In large equipment, the possible noise emitted by the outdoor unit: In these cases there are solutions such as the use of acoustic screens to confine the noise.